sql notes
6/18/24 • 9:44pm
Notes from SQL Tutorial - Full Database Course for Beginners
What is a Database (DB)?
- a collection of related information
- databases can be stored in different ways
- Computers + Databases = <3
- computers are great at keeping track of large amounts of information
- Database management Systems (DBMS)
- a special software program that helps users create and maintain a database
- makes it easy to manage large amounts of information
- handles security, backups, imports/exports, concurrency1
- interact with software applications, ex: programming languages
Amazon will tell the database management system to alter the database
C.R.U.D: Create, Read, Update, Delete
- Creating new entries
- Retrieving
- Updating
- Deleting
Core 4 operations
Any good DBMS can do these things
Two types of Databases
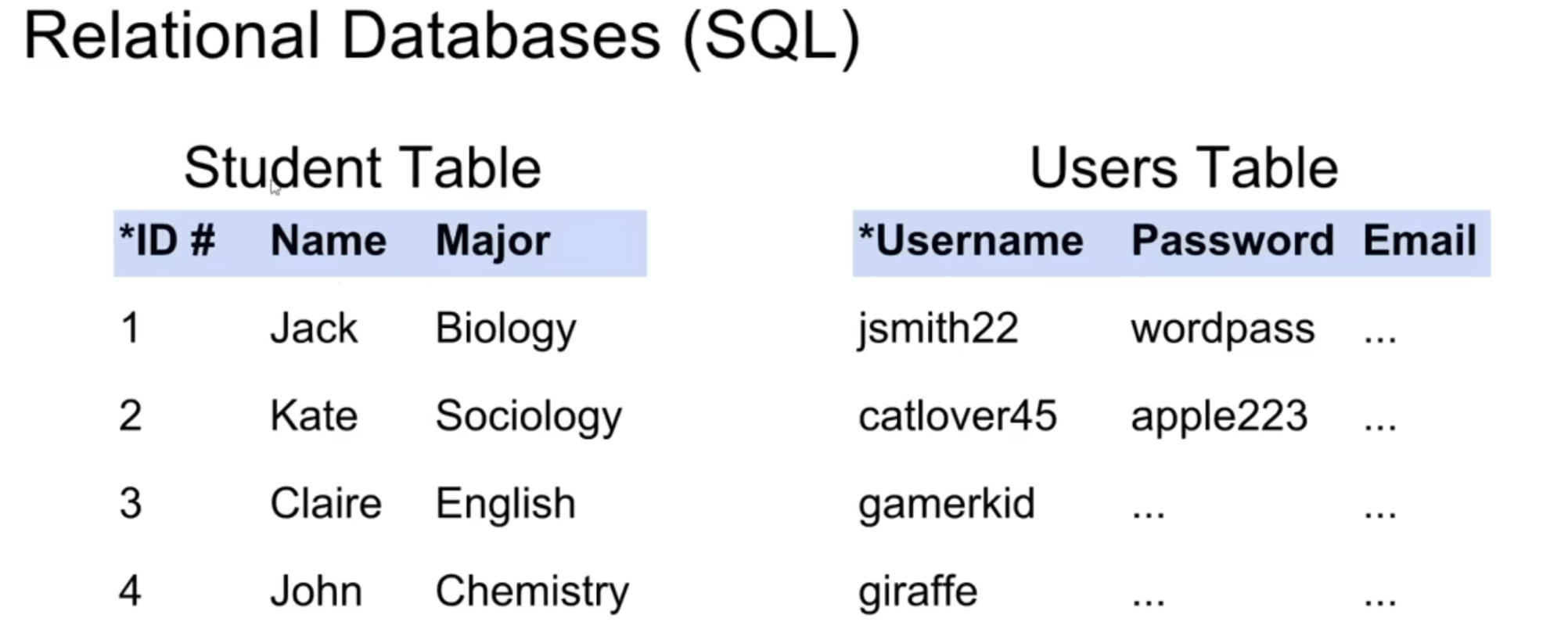
- Relational databases (SQL)
- organize data into one or more tables
- a unique key identifies each row
- Non-Relational databases (noSQL)
- organize data in anything but a table
- key value stores
- documents
-
json,xml, graphs
Relational databases
Can use a relational database management system (RDBMS)
- helps users create and maintain a relational database
- ex: mySQL, Oracle, postgreSQL, etc.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
- standardized lang for interacting with RDBMS
- used to perform CRUD operations
- define tables and structures
- SQL code used on one RDBMS may not be usable on another
SQL is the standard in relational databases
Non relational
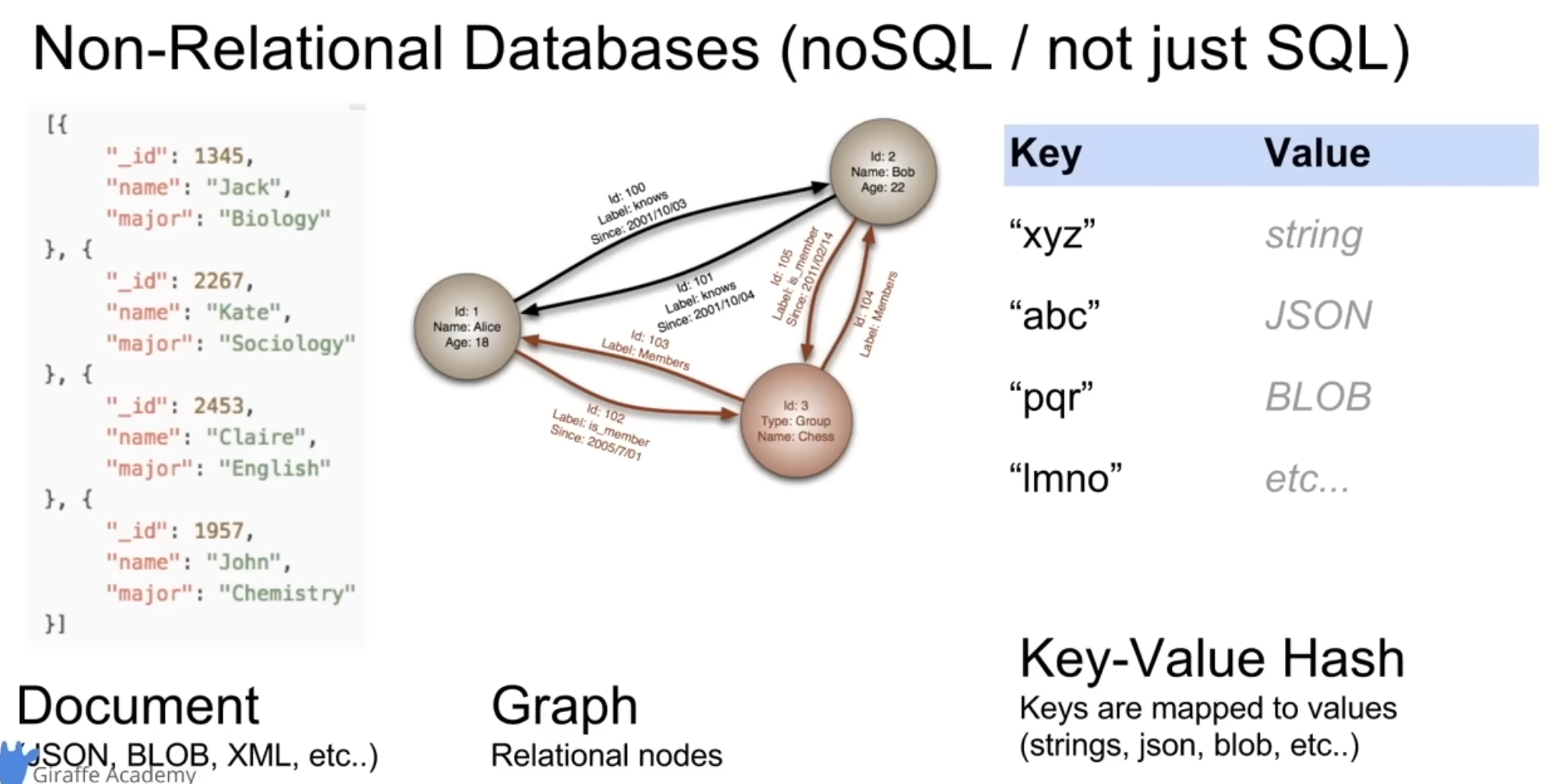
Management systems:
- MongoDB, firebase, etc.
- implementation specific -> no standard language
Database queries
- Queries
- are requests made to the database management system for specific information
As the structure becomes more complex, it becomes more difficult to get specific pieces of information
- Tables
- Have columns, rows
- Columns
- categories
- Rows
- a single entry
- Primary key
- uniquely defines a row
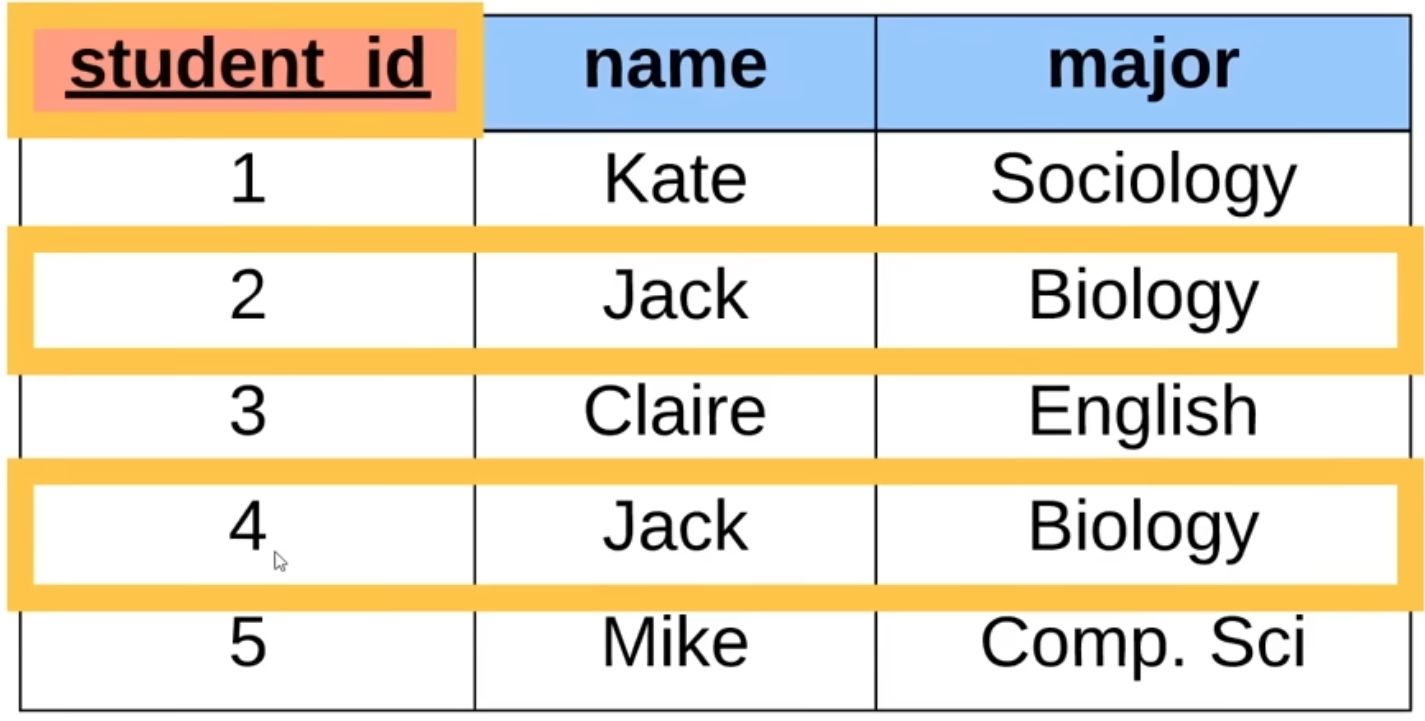 How to discern between the Jacks?
How to discern between the Jacks?
Primary key is different. Always going to be unique for each row in the table
Can be anything (str, int, etc.), as long as its unique
Types of Primary keys
-
- Surrogate key
- key that has no mapping to anything in real world (random)
-
- Natural key
- ex: social security number
-
- Foreign key
- stores the primary key of a row in another database table
Foreign key example:
branch_id maps to a row in the Branch database 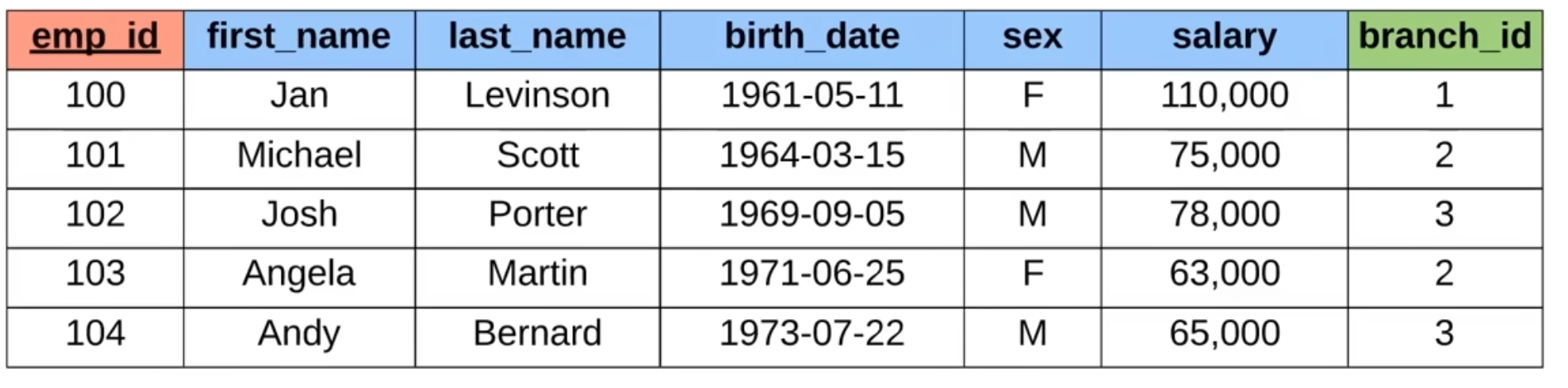
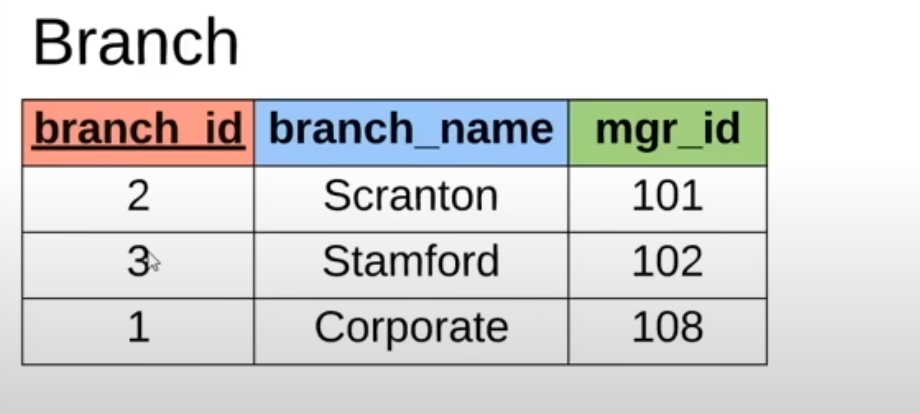
Note: can have multiple foreign keys
Can also use foreign key to map to another row in the same table
Can define a composite key to define a key that uses multiple columns to combine to make a primary key.
ie: two columns uniquely defining a row to make a primary key
6/19/24 • 9:10pm
SQL Basics
Not technically a programming language Language used for interacting with relational database management systems
- SQL
- structured query language
There are different “flavors” SQL
Sometimes different depending on the management system
4 aspects
- Data Query language (DQL)
- used to get data already stored
- Data definition language (DDL)
- define layout, schema
- Data control language (DCL)
- used for controlling access to the data in the database
- Data manipulation language (DML)
- used for inserting, updating, deleting data from the databases
Queries
Goal is to only get the data you need
Often hidden in a complex schema
Tell RDBMS what information you want and it will give it back to you
SELECT employee.name, employee.age
FROM employee
WHERE employee.salary > 3000;
MySQL installation
Install, set up and start server
$ echo "export PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bash_profile
^ appends mysql path to path accessible by bash command line 2
$ mysql -u root -p
enter password (logs into mysql as root)
create database giraffe;
Data types
-> using popSQL for visualization purposes
INT -- WHOLE NUMBERS
DECIMAL(M, N) -- DECIMAL NUMBERS (M - TOTAL NUM OF DIGITS) (N - NUM DIGITS AFTER DECIMAL POINT)
VARCHAR(1) -- STRING OF TEXT OF LENGTH 1
BLOB -- BINARY LARGE OBJECT, STORES LARGE DATA
DATE -- 'YYYY-MM-DD'
TIMESTAMP -- 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS' USED FOR RECORDING WHEN THINGS HAPPEN
Creating tables
CREATE TABLE -- convention is to use all caps for reserve words
Trying to create this table: 
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20), -- ALLOCATE FOR STORING A NAME
major VARCHAR(20)
); -- ALL COMMANDS SHOULD END IN ';'
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20),
PRIMARY KEY(student_id) -- can also define primary key like this
);
DESCRIBE student; -- prints the table you made
NOTE: that if you want to run this in the command line:
$ USE giraffe; DESCRIBE student;
I will be writing these commands in popSQL, but it is good to know how to run thing in the terminal
Delete and modify a table
DROP TABLE student; -- deletes the table
ALTER TABLE student ADD gpa DECIMAL(3, 2); -- add a row for gpa
-- 3 digits, 2 after the
-- decimal point
ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN gpa; -- drops the gpa column
inserting data
INSERT INTO student VALUES(1, 'Jack', 'Biology'); -- insert information into table
-- insert in the order table was created
SELECT * FROM student; -- gives us all info from student table
INSERT INTO student(student_id, name) VALUES(2, 'Lucas');
-- leaves major null and allows you to insert the known values
NOTE: you can’t insert duplicate entries
creating tables for ease of insertion
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- name can't be null
major VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE -- major has to be unique
);
PRIMARY KEY is both NOT NULL and UNIQUE
setting a default value and auto incrementing
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, -- data inserted will auto increment
-- starting from 1
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'undecided' -- default value
);
INSERT INTO student(name) VALUES('Jack');
-- values for id: 1, major: undecided
Updating and deleting tables
UPDATE student
SET major = 'Bio'
WHERE major = 'Biology'
;
Comparison ops
-
=equals -
<>not equals -
<less than -
>=greater than or equal -
<=less than or equals
-- updating
UPDATE STUDENT
SET major = 'Biochemistry'
WHERE major = 'Bio' OR major = 'Chemistry'
;
UPDATE STUDENT
SET name = 'Tom', major = 'undecided'
WHERE student_id = 1;
;
--- without WHERE, all students are affected
-- deleting
DELETE FROM student
WHERE student_id = 5
;
Basic Queries
Get specific entries from the relational database management system
SELECT * FROM STUDENT; -- selecting 'all information'
SELECT name FROM STUDENT; -- get just the names
SELECT name, major FROM STUDENT; -- get both names and majors
--- can also be written as
SELECT student.name, student.major;
-- displays students ordered by name
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT
ORDER BY name;
-- displays in ascending order
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT
ORDER BY name ASC;
-- displays order from major first, then name
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT
ORDER BY major, name;
-- only gives 2 results
SELECT *
FROM student
LIMIT 2;
-- use WHERE to specify
SELECT name, major
FROM student
WHERE major = 'Chemistry' OR name == 'Lucas';
-- comparison operators:
-- <, >, <=, >=, =, <>, AND, OR
-- use set of data to filter
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT
WHERE name IN ('Kaden', 'Lucas', 'Quin') and student_id > 2;
Complex schema
Moving on from basics and core concepts, moving towards applicable examples